Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) Explained
In recent years, Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) has gained significant attention as a treatment option for various conditions, particularly in the management of menopause symptoms. However, there is still a lot of confusion and misinformation surrounding this topic. In this article, we will delve into what Hormone Replacement Therapy is and how it works.
What is Hormone Replacement Therapy?
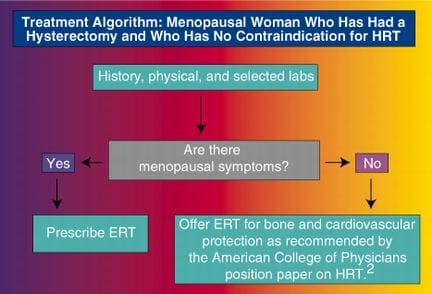
Hormone Replacement Therapy, or HRT, refers to the use of medication to supplement the hormones that the body can no longer produce in sufficient amounts. It is most commonly used to relieve menopause symptoms in women, but it can also be prescribed for other conditions like hypogonadism in men.
Types of Hormone Replacement Therapy
There are various types of Hormone Replacement Therapy available, depending on the specific needs and health condition of the individual. These may include: Estrogen-only Therapy: This type of HRT includes estrogen medication and is typically prescribed to women who have undergone a hysterectomy. Combined Estrogen-Progestin Therapy: This form of HRT combines both estrogen and progestin hormones and is usually prescribed to women who have not had a hysterectomy. Transdermal Therapy: Transdermal HRT involves delivering hormones through the skin via patches, creams, or gels. Bioidentical Hormone Therapy: Bioidentical hormones are chemically identical to the hormones naturally produced by the body. This type of HRT is custom-compounded according to an individual’s hormone levels and needs.
How Does HRT Work?
When hormone levels decline due to menopause or other conditions, it can lead to a wide range of symptoms like hot flashes, mood swings, osteoporosis, and vaginal dryness. HRT works by replenishing the hormones that are deficient, helping to alleviate these symptoms and improve quality of life. Estrogen replacement, for instance, can help reduce hot flashes, night sweats, and vaginal dryness. It can also improve bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis. Progestin, on the other hand, is often included in combined HRT to protect the uterus lining from overgrowth, which can increase the risk of uterine cancer in women with intact uteruses. However, it is important to note that HRT is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The decision to use HRT should be made on an individual basis after careful consideration of the person’s medical history, current health conditions, and potential risks and benefits.
Potential Risks and Benefits
Like any medication, Hormone Replacement Therapy carries both risks and benefits. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to weigh these factors before starting HRT. Some potential benefits of HRT include: Relief from menopause symptoms such as hot flashes, night sweats, and mood swings Improved bone health and reduced risk of osteoporosis Protection against colon cancer (for certain types of HRT) However, there are also potential risks associated with HRT, including: Increased risk of blood clots Elevated risk of heart disease Higher likelihood of breast cancer (with long-term use) These risks can vary depending on factors such as the type of HRT, the dosage, and the duration of treatment. Regular monitoring and follow-up with a healthcare provider are essential to minimize potential risks and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
Conclusion
Hormone Replacement Therapy can offer significant relief for individuals experiencing hormone deficiency-related symptoms, particularly menopausal women. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable type and dosage of HRT, taking into account individual health needs and weighing potential risks and benefits. With appropriate personalized care, Hormone Replacement Therapy can help improve quality of life for those in need.